

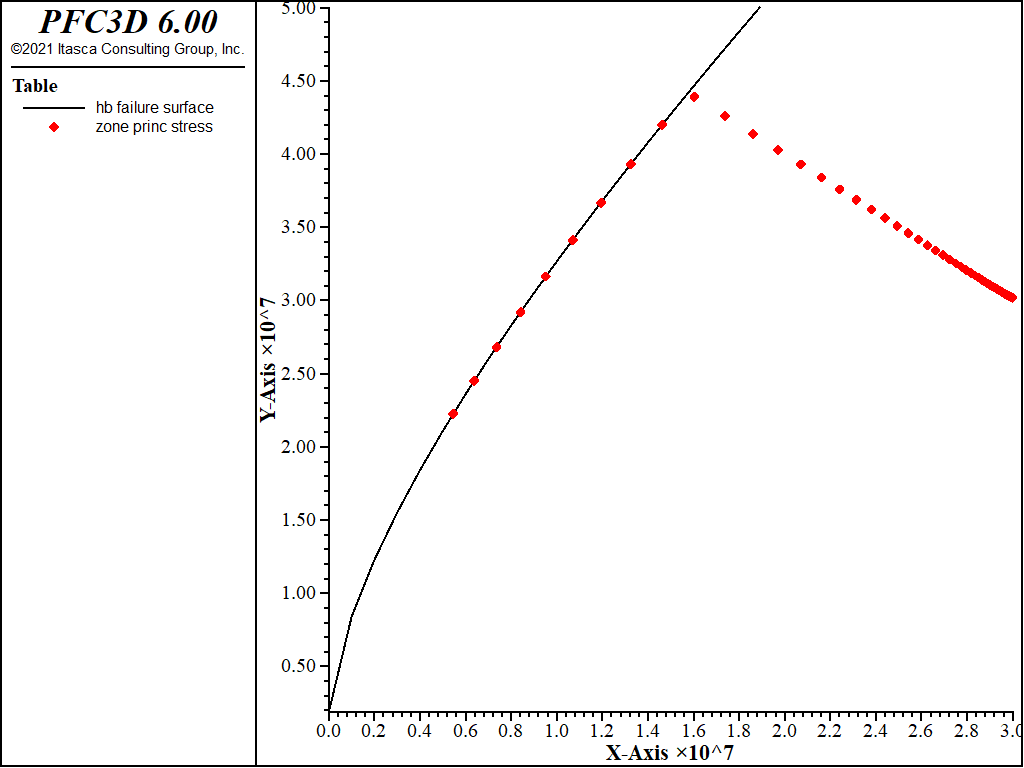
The case studies also demonstrate that the value of the FOS for a given slope will be significantly influenced by the boundary condition when the slope angle is less than 50°. Results show that the convergence criterion used in the 3D model plays an important role, not only in terms of the calculation of the factor of safety (FOS), but also in terms of the shape of the failure surface. In practice, the intermediate principal stress has certain influences on the strength of geomaterials (e.g., rock and soil) or concrete. Consideration of the HB is valid only for model volumes greater than the representative elementary volume (REV) of the geological strength index (GSI). The evaluation of the bearing capacity of footings usually does not take into account the effect of the intermediate principal stress. Next, the generalized Hoek-Brown (HB) failure criterion was used to model the rock mass strength and perform a Mohr-Coulomb equivalence, as shown by Hoek et al. The elasto-plastic Mohr-Coulomb criterion was used as a failure criterion throughout the analyses. The bearing capacity for footings is a fundamental scientific problem in civil engineering. Extensive case studies are carried out to investigate the influence of convergence criterion and boundary conditions on the 3D slope modeling. thickness) (Hoek & Brown, 1980 Hoek, Kaiser, & Bawden, 1993 Hoek, 2006), while the horizontal stress component was assumed to be equal to the vertical stress. scheme, FLAC3D (Cundall et al., 2003) and a number of finite element. In this research, therefore, a non-linear SSR technique is proposed that can use the Hoek-Brown (HB) criterion to represent the non-linear behavior of a rock mass in FLAC 3D program to analyze 3D slope stability. limitations of the HoekBrown empirical rock and rock mass strength criterion. However, it is known that rock mass strength is a non-linear stress function and that, therefore, the linear MC criterion does not agree with the rock mass failure envelope very well. Existing numerical modeling of three-dimensional (3D) slopes is mainly performed by the shear strength reduction (SSR) technique based on the linear Mohr-Coulomb (MC) criterion, whereas the non-linear failure criterion for rock slope stability is seldom used in slope modeling.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
